Folate Vs. Folic Acid: Which Is Best For Your Pregnancy?
Welcoming a new life into the world is an exciting and cherished journey. As an expectant mother, ensuring the health and development of your baby is a top priority. One crucial aspect of prenatal care is understanding the differences between folate and folic acid, and how they can impact your pregnancy.
The Vital Role of Folate in Pregnancy
Folate, a water-soluble B vitamin, plays a pivotal role in the healthy growth and development of your baby. It’s essential for the formation of DNA and RNA, which are critical for proper cell division. During pregnancy, folate is particularly crucial for the correct development of the neural tube, the structure that will ultimately become your baby’s brain and spinal cord.
Folate and Neural Tube Development
One of the most vital contributions of folate is its support for the healthy development of the neural tube. This structure closes within the first 28 days of pregnancy, often before many women realize they are expecting. Ensuring adequate folate intake during this critical period is essential for proper neural tube closure. Insufficient folate levels can lead to severe birth defects, such as spina bifida and anencephaly, which can have lifelong consequences for the child.
Statistics show that neural tube defects affect approximately 3,000 pregnancies in the United States each year. However, research demonstrates that women who consume sufficient amounts of folate before and during early pregnancy can significantly reduce their risk of these defects.
Additional Benefits of Folate
Beyond its crucial role in neural tube development, folate offers numerous other benefits for pregnant women. It assists in the formation of red blood cells, helping to prevent anemia, a common condition during pregnancy. Furthermore, folate supports healthy cell division and contributes to the synthesis and repair of DNA, which is vital for both maternal and fetal health.
Understanding Folate and Folic Acid
Folate and folic acid are often used interchangeably, but they are not exactly the same. Folate is the natural form of the vitamin found in various foods, while folic acid is the synthetic version commonly used in supplements and fortified products.
Folate: The Natural Form
Folate occurs naturally in a variety of foods, including leafy green vegetables, beans, lentils, and citrus fruits. This natural form of the vitamin is readily absorbed by the body and plays a crucial role in overall health.
Folic Acid: The Synthetic Counterpart
Folic acid, on the other hand, is the synthetic version of folate. It was introduced into the U.S. food supply in 1998 through mandatory fortification of grain products, with the goal of combating the rising incidence of neural tube defects. Folic acid’s stability and cost-effectiveness make it a popular choice for fortification in products like breakfast cereals, bread, and pasta.

Pros and Cons of Folic Acid
Folic acid has several advantages, such as its stability, effectiveness in increasing blood folate levels, and proven role in preventing neural tube defects. However, there are also some drawbacks to consider:
- Synthetic Nature: Unlike folate, which occurs naturally in foods, folic acid is man-made.
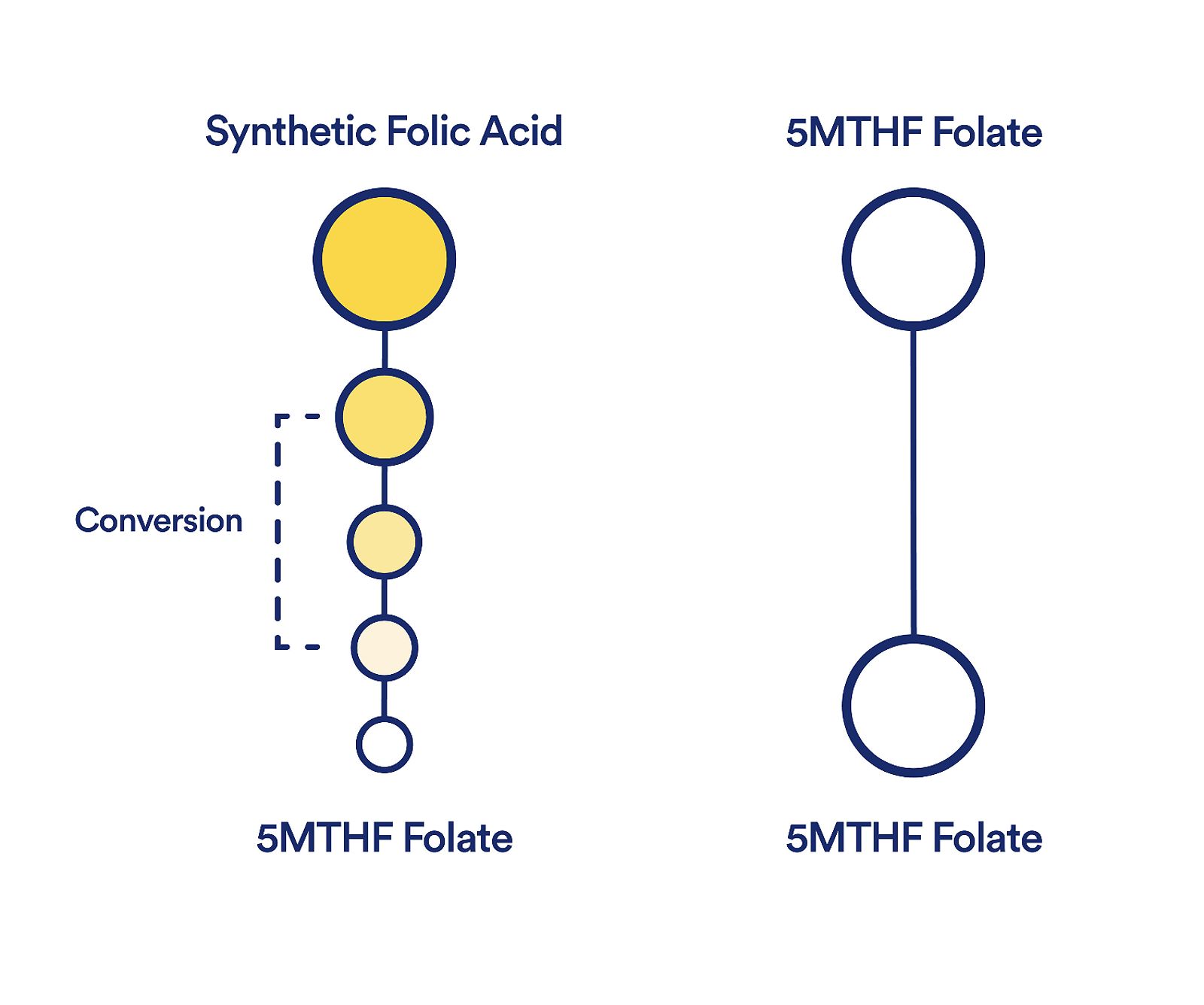
- Conversion Issues: Some individuals may have difficulty converting folic acid into its active form, 5-MTHF, which can limit its effectiveness.
- Potential Excess: High levels of unconverted folic acid in the body could lead to negative health effects.
The MTHFR Gene Variation and Folate Metabolism
One important factor to consider when choosing between folate and folic acid is the MTHFR gene variation. Approximately 30-50% of the population carries a common variant of this gene, which can impede the conversion of folic acid into its active form, 5-MTHF. Individuals with this variation may benefit more from taking 5-MTHF supplements instead of folic acid.
Making an Informed Choice
When it comes to folate vs. folic acid for pregnancy, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best option for your individual needs. Consider the following factors:
- MTHFR Variations: If you have the MTHFR gene variation, you may want to opt for 5-MTHF supplements instead of folic acid.
- Prenatal Vitamin Selection: When choosing a prenatal vitamin, look for one that specifically mentions 5-MTHF or methylfolate if you have the MTHFR variation.
- Recommended Intake: The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for folate during pregnancy is 600 mcg DFE (Dietary Folate Equivalents) per day.
- Timing and Sources: Start folate supplementation at least one month before conception and continue throughout pregnancy. Incorporate a variety of folate-rich foods into your diet as well.

Optimizing Folate Intake for Your Pregnancy
To ensure you’re getting the recommended amount of folate during your pregnancy, you can consider the following strategies:
Folate-Rich Foods
Incorporate a variety of folate-rich foods into your diet, such as:
- Leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale, broccoli)
- Beans, lentils, and peas
- Citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruit)
- Avocados
- Fortified cereals and breads
These natural sources of folate can help you meet your daily needs.
Folate Supplements
If you’re unable to get enough folate from your diet, or if you have the MTHFR gene variation, consider taking a folate supplement. Look for prenatal vitamins that contain the recommended amount of folate or 5-MTHF.
Timing and Consistency
Start taking folate supplements at least one month before conception and continue throughout your pregnancy. Consistent intake is crucial for supporting your baby’s neural tube development and overall health.
Folate Beyond Pregnancy
Adequate folate intake is not only crucial during pregnancy but also plays a significant role in long-term health for both mothers and children. Folate is essential for brain development and cognitive function in children, impacting their growth and learning abilities.
Research also suggests that folate deficiency can lead to long-term health issues, including cardiovascular diseases and stroke. Maintaining a diet rich in folate throughout your life can have lasting benefits for you and your child.
FQAs
What are some good sources of folate in my diet?
Excellent sources of folate include leafy green vegetables, beans, lentils, citrus fruits, and fortified cereals.
Can I take too much folic acid?
While folic acid is essential, excessive intake can lead to negative health effects. It’s important to adhere to the recommended guidelines and consult with your healthcare provider about appropriate dosage.
Should I get tested for the MTHFR gene variation?
If you have concerns about folate metabolism or a family history of related health issues, consulting with a healthcare provider about testing for the MTHFR gene variation may be beneficial.
How can I find a prenatal vitamin with 5-MTHF?
Look for prenatal vitamin labels that specifically mention 5-MTHF or methylfolate, especially if you have the MTHFR gene variation.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between folate and folic acid is essential for pregnant women. Adequate folate intake can significantly reduce the risk of neural tube defects and support overall maternal and fetal health. By consulting with your healthcare provider and making informed choices about prenatal nutrition, you can ensure that you and your baby receive the vital nutrients needed for a healthy start.
MORE FROM animalswik.com